Distributed Energy Resource Management System (DERMS)
August 2, 2024
What is DERMS?
Distributed energy resources management system (DERMS) is a system that helps manage, monitor and optimize the use of different kinds of energy sources that are scattered across a larger area, like solar panels on rooftops, wind turbines in different locations, energy storage batteries, and even small-scale power generators. These energy sources are called distributed energy resources (DERs).
Think of DERMS as a smart brain that connects and coordinates all these DERs, making sure they work together efficiently. It collects information from each DER, like how much energy they’re producing, when they’re producing it, and how much they’re using. With this data, DERMS can make decisions to balance energy supply and demand, reduce waste, and even help the grid handle unexpected events like power outages more smoothly.
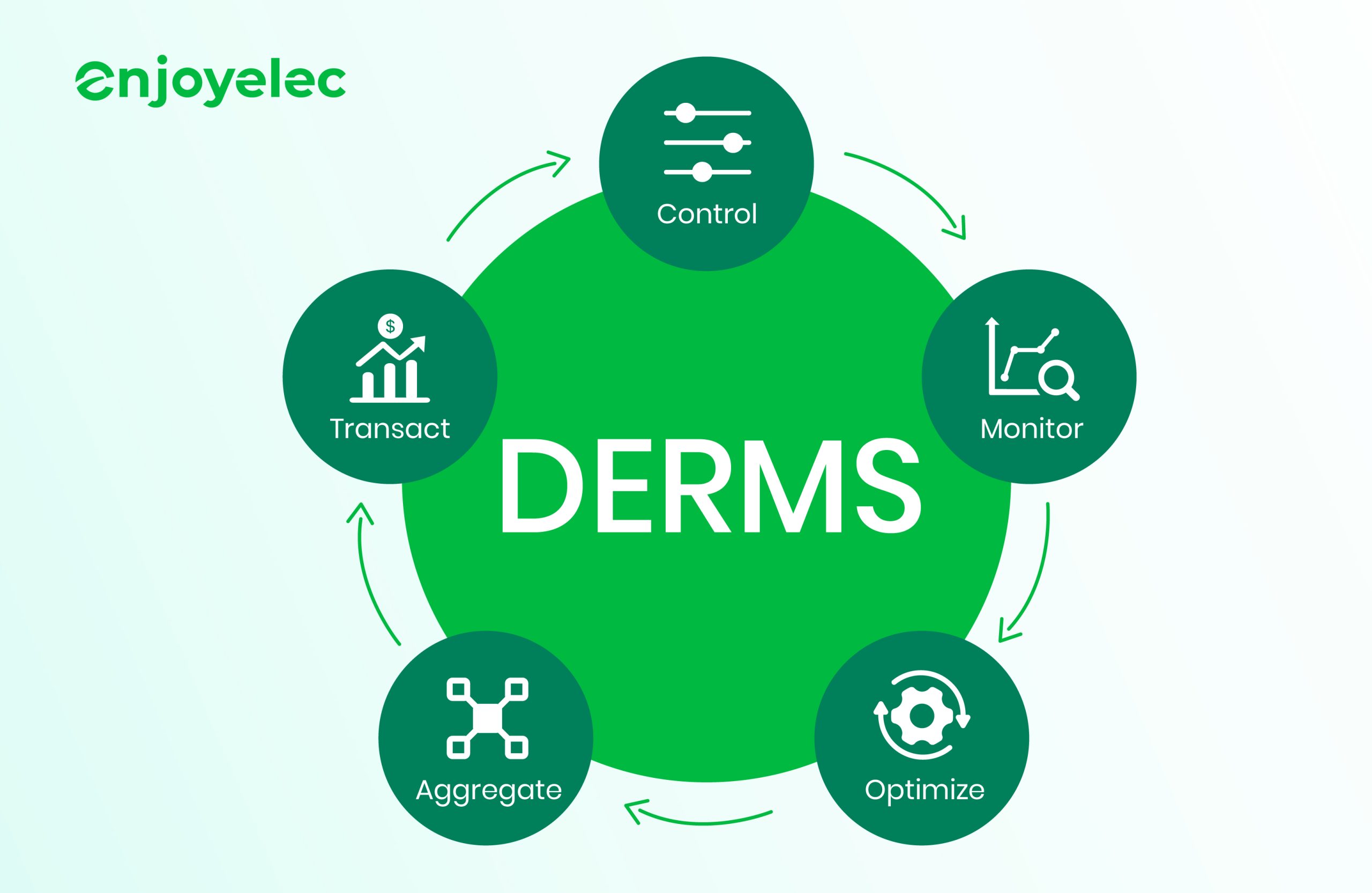
Benefits of Implementing DERMS
-
Seamless Renewable Energy Integration: DERMS facilitate the smooth incorporation of renewable energy sources like solar and wind, promoting a greener and more sustainable energy ecosystem.
-
Enhanced Grid Stability: By improving grid stability and resilience, DERMS minimize the risk of outages and ensure a consistent and reliable energy supply.
-
Increased Flexibility: DERMS offer enhanced flexibility in energy management, enabling users to quickly adapt to evolving energy demands and conditions.
Applications of DERMS
DERMS offers a versatile range of applications that enhance energy efficiency, grid stability, and cost savings across various sectors:
-
Home Energy Management Systems (HEMS): Managing home inverters, batteries, smart meter, HVAC and EV chargers to optimize energy use. By monitoring and managing household energy consumption, HEMS helps reduce energy waste and lowers electricity bills.
-
Energy Trading: Aggregating the output of distributed energy resources, enabling participation in energy markets as a single entity.
-
Dynamic tariffs: Our system leverages OpenADR to track dynamic electricity pricing, intelligently scheduling device usage to take advantage of lower rates.
-
EV charging: Coordinating the charging of electric vehicles (EVs) to prevent grid overload and capitalize on low-cost, off-peak electricity. Enabling V2G technology, allowing EVs to supply power back to the grid during high-demand periods, providing additional grid support.
Difference between DERMS and VPP
Virtual Power Plants (VPP) and Distributed Energy Resource Management Systems (DERMS) both play crucial roles in managing and integrating Distributed Energy Resources (DERs) with the grid and market systems. They help optimize grid operations and provide essential services, coordinating both individual and grouped DERs. However, there are some subtle differences worth noting.
Key Differences:
- VPP: Virtual Power Plants focus on controlling power across a network of assets to deliver grid services. These services are not heavily dependent on the exact location of individual assets. VPPs typically provide system-wide benefits by scaling up or down the generation or load, catering to broader regions such as ISO (Independent System Operators) and RTO (Regional Transmission Organizations) areas.
- DERMS: Distributed Energy Resource Management Systems deliver grid services closely tied to the specific location of each asset. DERMS manage power flows along individual feeders and provide services like voltage management, optimal power flow, and locational capacity relief. They manage both real power (watts) and reactive power (VARs), allowing for precise control of load and generation on specific sections of the grid.
- VPP: Engage in active power control to deliver grid services without a strong reliance on the specific location of assets. They focus on aggregate benefits over a wider area.
- DERMS: Provide location-specific control of power flows, adjusting both real and reactive power to optimize performance on individual feeders.
- VPP: Typically offer services that benefit the entire grid, such as balancing supply and demand, reducing peak load, and integrating renewable energy sources.
- DERMS: Offer services that are more localized, including voltage control, power flow optimization, and providing capacity relief in specific areas of the grid.
4、Operational Differences:
- VPP: Often operate over larger geographic areas and are integrated with market operations to participate in energy trading and grid balancing across wide regions.
- DERMS: Focus on the distribution network, optimizing power flows and managing resources within specific, localized sections of the grid.
In summary, while both VPP and DERMS manage and coordinate DERs for grid integration, VPP are more about broad, system-wide control and benefits, whereas DERMS provide precise, location-specific management and optimization of the grid.
The Role of AI in DERMS
Human decision-making alone cannot fully exploit the potential of even the most advanced distributed energy resource management systems (DERMS). Grid operators and asset managers already struggle with meeting demand using the resources under their direct control, let alone managing thousands of edge devices and processing immense amounts of real-time data.
This is where artificial intelligence (AI) comes in. AI excels at handling Big Data, continuously monitoring edge devices and making real-time decisions about resource allocation. It takes into account current demand, supply, weather conditions, and other dynamic factors. At enjoyelec, our AI-driven energy solutions also leverage historical data analysis and predictive modeling to create accurate forecasts of future electricity price. This enables our AI software to optimize and control devices, ensuring that electricity is delivered smoothly at the right time and cost.
An effective analogy for AI’s role in DERMS can be seen in modern traffic management systems. Many cities now use AI to coordinate traffic lights, equipped with sensors to collect data and receivers to process instructions. This technology helps minimize congestion and improve traffic flow. Similarly, in energy management, AI integrates and manages distributed energy resources, enhancing grid stability and efficiency.
The Role of DERMS in Smart Gird
A Distributed Energy Resource Management System (DERMS) plays a pivotal role in the functioning of a smart grid. As modern energy systems become increasingly complex with the integration of renewable energy sources and distributed energy resources (DERs), the need for advanced management systems like DERMS becomes essential.
Key Functions of DERMS in a Smart Grid:
-
Integration of Renewable Energy: DERMS seamlessly integrates various renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, into the grid. It manages the intermittent nature of these resources, ensuring a stable and reliable energy supply.
-
Real-Time Monitoring and Control: By continuously monitoring DERs, DERMS provides real-time data on energy production, consumption, and storage. This allows for immediate adjustments to maintain grid stability and efficiency.
-
Optimization of Energy Resources: DERMS optimizes the use of all available energy resources. It balances supply and demand, reduces energy wastage, and ensures that energy is delivered at the most cost-effective times.
-
Enhanced Grid Reliability and Resilience: By managing distributed energy resources, DERMS enhances the reliability and resilience of the grid. It can quickly respond to disruptions, such as power outages or sudden changes in energy demand, ensuring minimal impact on consumers.
-
Support for Demand Response Programs: DERMS enables demand response programs, where energy consumption is adjusted in response to supply conditions. This helps in reducing peak demand and shifting energy usage to off-peak times, thus lowering energy costs and improving grid efficiency.
What does the future look like for DERMS?
The evolution of energy management is increasingly centered around the use of DERMS. As we transition to a more decentralized and renewable energy framework, DERMS will be essential in optimizing the efficiency, reliability, and sustainability of our energy systems.
The future of DERMS is increasingly intertwined with advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML). These technologies are being integrated into DERMS solutions to boost forecasting accuracy, optimize system operations, and enable autonomous decision-making. By leveraging AI and ML, DERMS will become even more adept at managing complex energy systems and adapting to real-time conditions.
Adopting DERMS is more than just a technological upgrade; it’s a crucial step towards advancing a cleaner and greener future. By integrating these sophisticated systems, we can develop a robust and flexible energy infrastructure that meets the demands of a growing population and adapts to the challenges of a changing climate.
Are you ready to take the next step in energy management? Download the HEMS app now to learn more:
📱App Store: https://apps.apple.com/us/app/enjoyelec/id6467418530
📱Google Play:https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.enjoyelec.hems
Connect with us at http://www.linkedin.com/company/enjoyelec for the latest updates, insights, and news. We look forward to engaging with you and sharing our journey towards a smarter energy future.🎉🎊
Subscribe to our free newsletter



