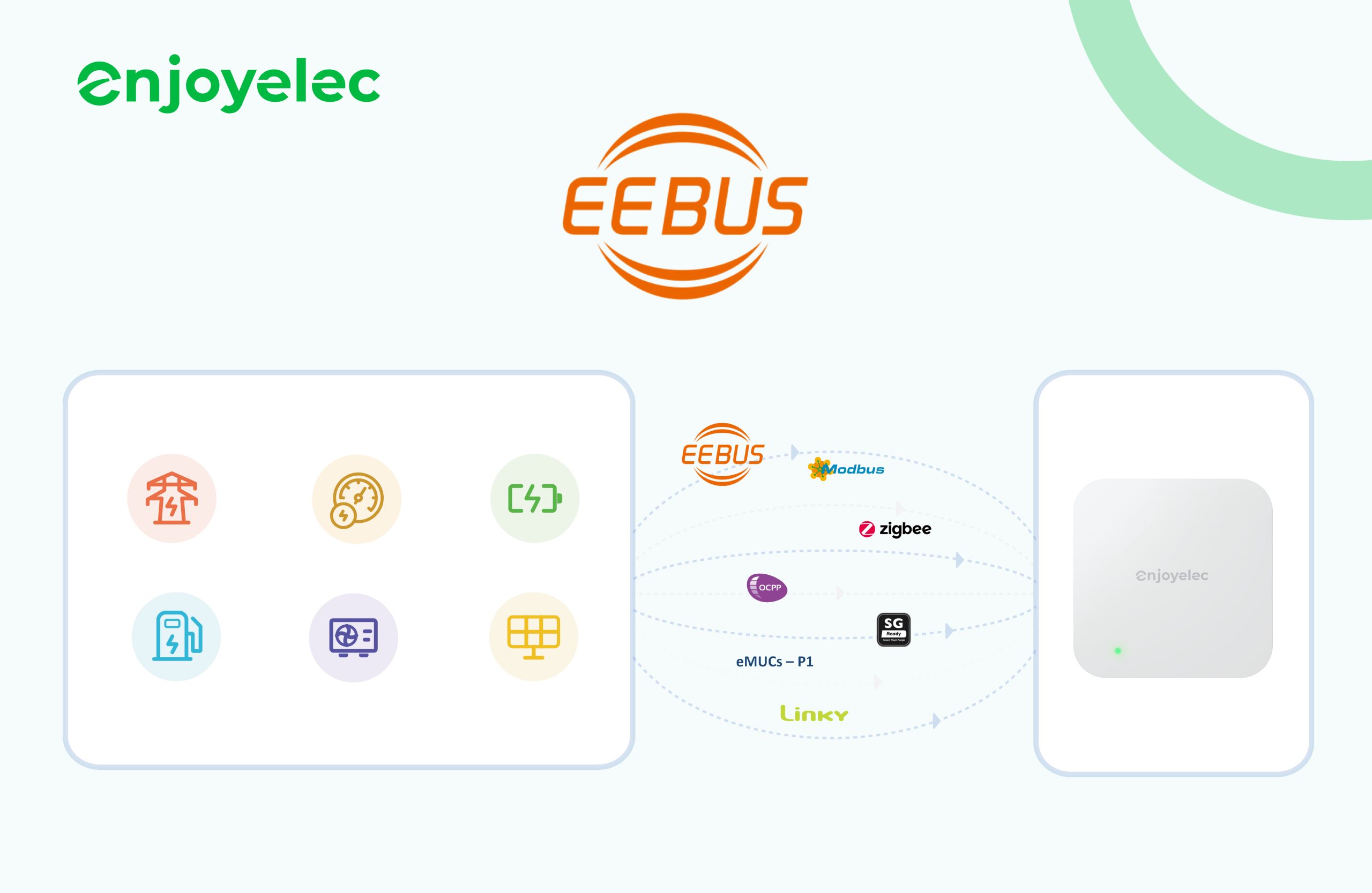
Peak Shaving: Smart Energy Savings
What is peak shaving?
Peak shaving is a method used to manage and reduce electricity consumption during periods of high demand, known as peak times. These peak periods occur when large numbers of consumers use substantial amounts of electricity at the same time, which can drive up costs and place additional pressure on the electrical grid. By reducing energy use during these critical times, peak shaving helps to smooth out the demand on the grid and avoid spikes in energy consumption.
Typically, peak shaving involves either cutting back on electricity usage during peak periods or shifting to alternative energy sources, such as drawing power from battery storage systems or renewable sources like solar panels. This allows businesses and homeowners to minimize their reliance on the grid when demand is highest, helping to stabilize energy use.
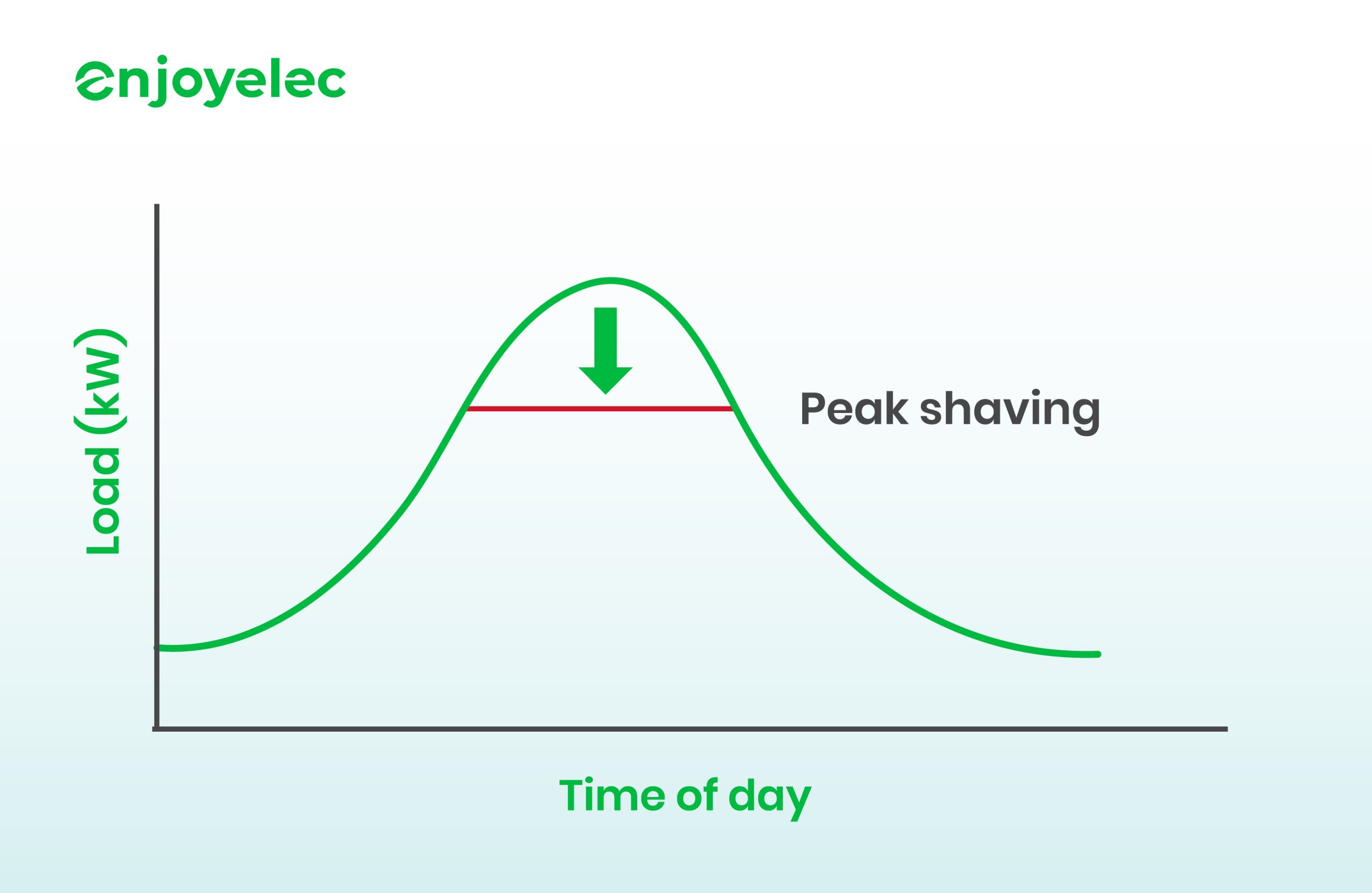
How does peak shaving work?
To prevent sudden spikes in electricity demand that strain the power grid and require expensive infrastructure upgrades, energy providers impose demand charges on commercial and industrial customers. These charges are based on a business’s peak electricity usage during a billing period, in addition to the standard cost of energy consumed. Demand charges encourage businesses to manage their energy consumption more efficiently, helping to stabilize the grid and avoid costly expansions.
For instance, let’s look at two restaurants that both consume 30,000 kWh of electricity in a month. Restaurant A has a peak demand of 90 kW, primarily during busy evening hours when patrons flood in. Meanwhile, Restaurant B spreads its energy use more evenly throughout the day, with a peak demand of just 40 kW. If the peak demand fee is $5 per kW, Restaurant A would face an additional cost of $450 for its peak demand, while Restaurant B would only pay $200. Despite their equivalent total energy consumption, Restaurant A ends up paying $250 more due to its higher peaks. This pricing structure encourages Restaurant A to find ways to manage its energy usage more effectively to reduce costs.
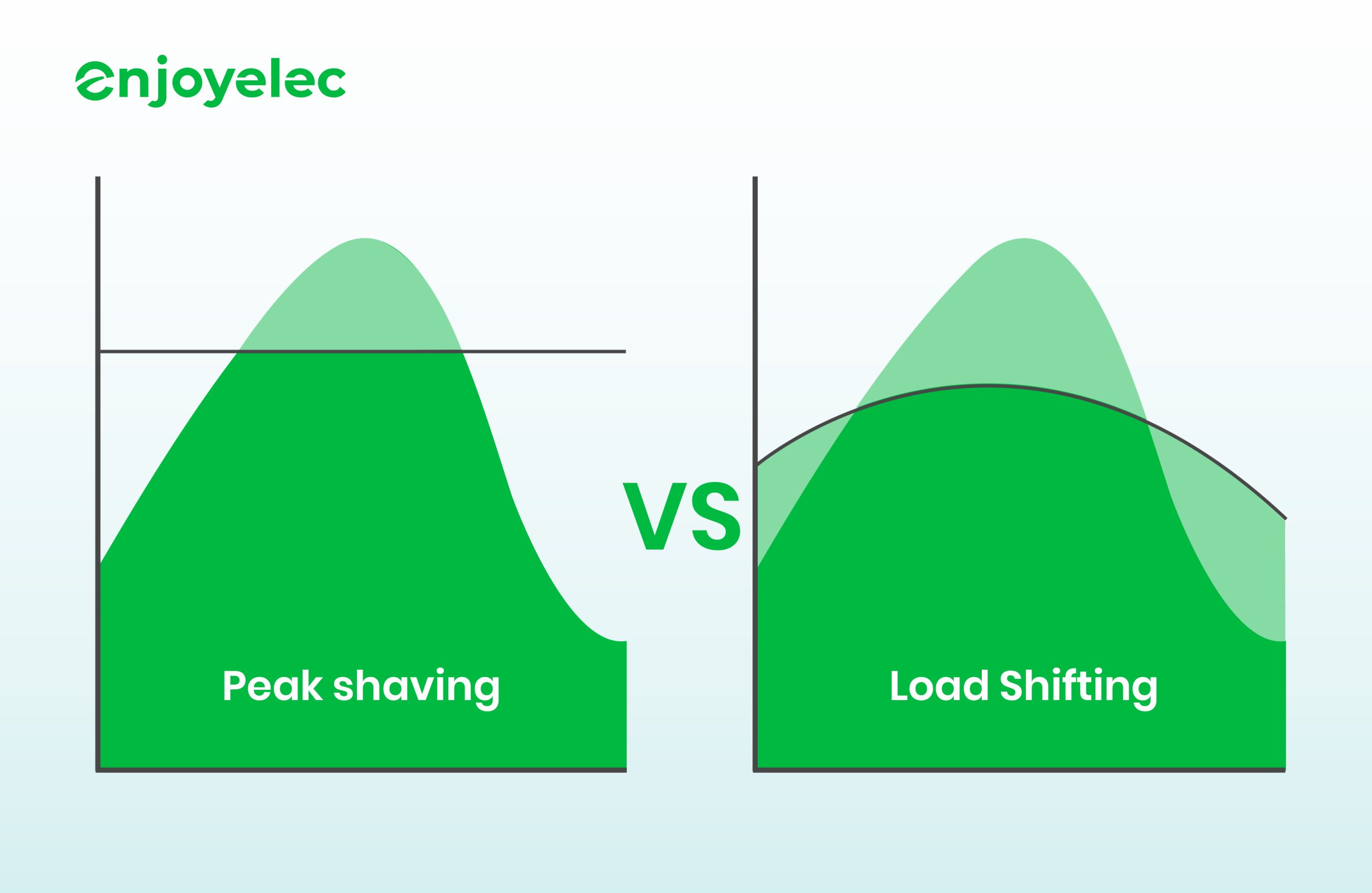
Peak Shaving vs Load Shifting: Choosing the Right Energy Strategy
Understanding the differences between peak shaving and load shifting is crucial for effective energy management in today’s dynamic energy landscape. Both strategies enhance demand-side flexibility but approach energy consumption in distinct ways. Peak shaving focuses on managing peak loads to reduce overall electricity consumption from the grid during high-demand periods, while load shifting optimizes energy usage based on pricing or grid conditions without decreasing total consumption.
Peak shaving is typically implemented by reducing electricity use during peak demand hours, which are often associated with higher electricity rates. This can involve adjusting operational schedules, temporarily shutting down non-essential equipment, or relying on backup energy sources like batteries or generators. By lowering peak demand, facilities can avoid costly demand charges imposed by utility companies, thus leading to significant savings on energy bills.
On the other hand, load shifting entails moving energy-intensive tasks to off-peak periods when electricity prices are lower. This strategy is particularly useful for facilities with flexible operations that can easily adjust their energy usage schedule. For instance, production processes or equipment can be programmed to operate during off-peak hours, thereby optimizing energy costs without changing the overall consumption profile.
So, what does this mean for your facility? For many industrial operations, peak shaving often proves to be the most advantageous choice. By lowering heavy demand charges and reducing overall energy consumption, it allows facilities to maintain their operations without interruptions. This is particularly important for those with inflexible loads, such as essential HVAC systems or critical machinery that must run continuously—tasks that cannot be easily shifted to off-peak hours.
Additionally, employing a combination of peak shaving and load shifting can provide a more comprehensive energy management strategy. For example, facilities can implement load shifting strategies for certain processes while simultaneously employing peak shaving techniques to manage unavoidable peak demands. This hybrid approach maximizes energy efficiency and cost savings while contributing to the overall stability of the electrical grid.
The benefits of peak shaving
By implementing peak shaving strategies, energy systems can unlock a range of advantages that enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and promote sustainability.
-
Grid Stability: Peak shaving reduces strain on the grid during high-demand periods, balancing electricity supply and demand. This minimizes the risk of blackouts and grid overloads, ensuring a reliable and stable power supply.
-
Cost Savings: Peak electricity prices rise due to increased demand. By reducing energy consumption during peak hours, businesses and consumers can avoid high costs, leading to significant savings on energy bills.
-
Efficient Resource Use: Peak shaving enhances energy efficiency by leveraging energy storage, demand response, and distributed energy resources. This reduces the need for traditional power plants to meet peak demand and smooths out energy consumption patterns.
-
Environmental Benefits: By lowering dependence on fossil-fuel power plants during peak times, peak shaving reduces greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. This contributes to a cleaner, more sustainable energy system.
-
Boosting Renewable Energy: Peak shaving facilitates renewable energy integration by storing excess solar and wind power during low-demand periods and using it during peak times. This helps mitigate the intermittency challenges of renewables, promoting cleaner energy use.
Application of peak shaving
Peak shaving is a practical strategy aimed at reducing electricity consumption during high-demand periods, helping companies cut costs and relieve stress on the electrical grid. Here are several approaches businesses can implement for peak shaving, based on real-world applications:
1. Energy Storage Systems (ESS):
Batteries are increasingly used in peak shaving applications. Energy storage systems store excess power during low-demand, low-cost periods (off-peak) and discharge the stored energy during peak demand periods. This can also work in conjunction with renewable energy sources like solar panels, where excess energy generated during the day is stored for use during peak hours.
2. Demand Response Programs:
Peak shaving is closely tied to demand response (DR), where users voluntarily reduce energy consumption during grid peak periods in exchange for financial incentives or lower electricity rates.By participating in these programs, consumers can automatically or manually lower consumption, contributing to grid stability while also benefiting from lower costs.
3. Microgrids and Distributed Energy Resources (DERs):
Microgrids and local energy generation sources (e.g., rooftop solar) help achieve peak shaving by reducing reliance on the central grid during peak demand times.These systems can switch to local power generation or stored energy during peak hours, reducing the load on the central grid and enhancing energy resilience.
4. Optimizing HVAC and Lighting Loads
For commercial buildings, heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, along with lighting, often account for a significant portion of energy consumption. By adjusting HVAC operations or dimming non-essential lighting during peak times, businesses can significantly reduce their peak energy demand, contributing to both cost savings and grid stability.
5. Electric Vehicle (EV) Integration:
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology allows EVs to discharge stored electricity back into the grid during peak periods, thus acting as a temporary energy storage solution.V2G systems can support peak shaving by enabling EVs to store energy when demand and rates are low and release that energy during peak times, helping balance supply and demand.
These methods highlight how peak shaving can be implemented across various energy systems to help businesses lower operational costs, enhance energy efficiency, and support the broader grid.
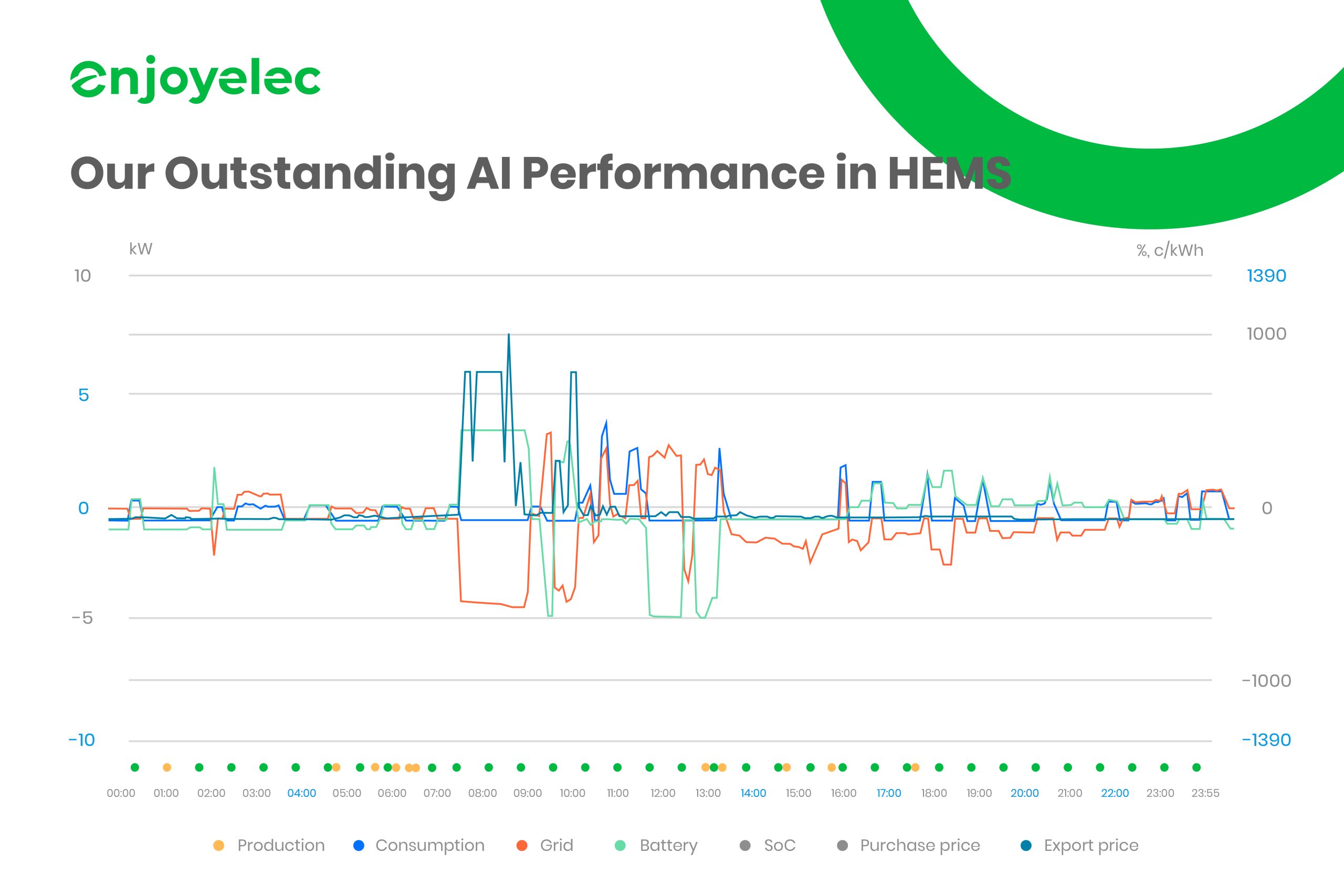
Peak Shaving Case Study: How enjoyelec’s AI-Powered HEMS Optimizes Energy Use
At enjoyelec, we’re thrilled to share a real-world case from Australia that demonstrates the power of our AI-driven Home Energy Management System (HEMS) in optimizing energy consumption and maximizing profits.
In this example, the energy dynamics between 7 AM and 10 AM showed significant fluctuations with multiple peaks in electricity prices. Our HEMS AI accurately forecasted these price surges and automatically discharged the battery, selling power back to the grid at the highest prices. This not only helped users avoid high electricity costs but also allowed them to generate additional income by capitalizing on peak pricing.
As the morning progressed and export prices dropped around 10 AM, with photovoltaic (PV) systems starting to produce electricity, the HEMS AI seamlessly transitioned into recharge mode. It intelligently instructed the home battery to recharge using both solar energy and the grid, ensuring the battery was optimally managed for the day without any manual input.
This case study highlights how enjoyelec’s AI technology doesn’t just save users money on electricity bills—it actively helps them earn profits by leveraging peak shaving and smart energy management. Throughout the day, the system continues to monitor price changes, efficiently scheduling energy use, and maximizing opportunities for cost savings and income generation.
The future of peak shaving
Peak shaving is set to play a crucial role in the evolving landscape of energy management and grid stabilization, particularly as renewable energy sources continue to gain prominence. By strategically reducing energy consumption during peak demand periods, peak shaving helps alleviate stress on the grid, lowers energy costs for consumers, and enhances the overall efficiency of power distribution. Advanced technologies, such as smart grids and demand response systems, will enable more effective implementation of peak shaving strategies. These systems allow for real-time monitoring and automated adjustments in energy usage, ensuring that consumers can optimize their consumption patterns based on dynamic tariff and grid conditions.
Looking ahead, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning will further enhance the capabilities of peak shaving initiatives. These technologies will analyze historical data and predict energy usage trends, allowing for proactive measures to be taken before peak periods occur. Additionally, the widespread adoption of energy storage solutions will provide a buffer against demand surges, enabling users to store energy during off-peak times and release it when demand spikes. As regulatory frameworks evolve and incentivize peak shaving, businesses and households will increasingly recognize its benefits, contributing to a more resilient and sustainable energy future.
Download the HEMS app now to learn more about peak shaving and how it can help you optimize your energy consumption.


Connect with us at http://www.linkedin.com/company/enjoyelec for the latest updates, insights, and news. We look forward to engaging with you and sharing our journey towards a smarter energy future.