What is a heat pump?
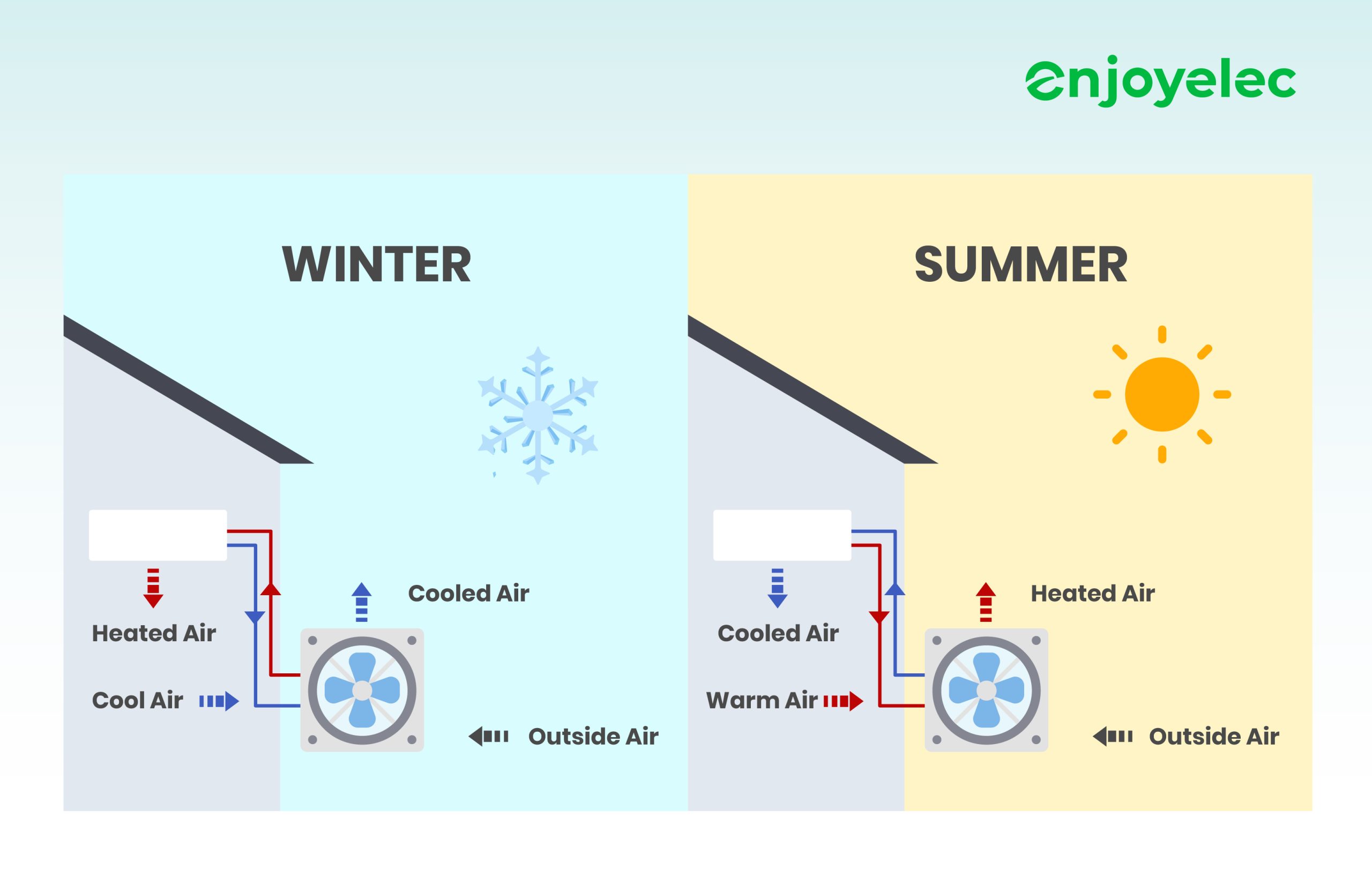
A heat pump is a versatile device designed to transfer heat from one location to another, offering both heating and cooling solutions for homes and businesses. During colder months, it extracts heat from the outside air, ground, or water and moves it indoors, effectively warming the space. In warmer months, the process reverses, allowing the heat pump to function as an air conditioner by removing heat from inside and releasing it outside.

How does a heat pump work?
In cooling mode, the process reverses. The refrigerant absorbs heat from inside the home, evaporating in the indoor coil. The compressor sends this heated gas outside, where it releases the heat and condenses back into a liquid. This continuous cycle allows the heat pump to provide efficient heating and cooling for residential and commercial spaces.
Three Types of Heat Pumps
There are three main types of heat pumps: air source, ground source, and water source. Each type has its unique advantages and applications, making them suitable for different environments.
1. Air Source Heat Pumps
Air source heat pumps are the most widely used type of heat pump. They extract heat from the outside air and are capable of both heating and cooling. During winter, these systems absorb heat from the air and transfer it indoors, while in summer, they reverse the process to provide cooling. Air source heat pumps are relatively easy to install and work effectively in moderate climates, making them a popular choice for homeowners looking for an energy-efficient solution.
2. Ground Source Heat Pumps (Geothermal)
Ground source heat pumps, also known as geothermal heat pumps, utilize the stable temperatures of the ground or groundwater for heating and cooling. These systems consist of underground loops that exchange heat with the earth. Although the installation process can be more expensive due to the excavation required, ground source heat pumps offer high efficiency and significant long-term energy savings. They are particularly beneficial in regions with extreme temperatures, as they provide consistent performance year-round.
3. Water Source Heat Pumps
Water source heat pumps draw heat from a nearby water source, such as a lake, river, or well. These systems are efficient and provide reliable heating and cooling. However, their effectiveness depends on the availability of suitable water sources. Installation may require special considerations and adherence to local regulations. Water source heat pumps are an excellent option for properties located near bodies of water, offering a sustainable heating and cooling solution.
The Difference Between Heat Pumps and Air Conditioners
Heat pumps and air conditioners are both popular options for climate control in homes, but they serve different functions and operate in distinct ways.
- Functionality
Heat pumps are designed for both heating and cooling. In winter, they extract heat from the outside air (even in low temperatures) and transfer it indoors, providing efficient heating. In summer, they can reverse this process, functioning like an air conditioner. This dual functionality makes heat pumps an ideal choice for European climates, where seasonal temperature variations are significant.
On the other hand, traditional air conditioners are primarily designed for cooling. They absorb heat from indoors and expel it outside, making them effective for hot summer months but unsuitable for heating during colder seasons. While some air conditioners offer heat pump capabilities, many models do not provide heating.
- Energy Efficiency
Heat pumps are generally more energy-efficient than traditional air conditioning systems. They move heat rather than generate it, which means they can provide more heating or cooling energy than the electrical energy they consume.
- Installation and Cost
While both systems require professional installation, heat pumps may involve a higher upfront cost due to their dual functionality and more complex technology. However, the long-term savings on energy bills and maintenance can make heat pumps a more economical choice over time.
Growing Market Share of Heat Pumps in Europe
In several countries where heating predominantly relies on fossil fuels, heat pumps have been steadily increasing their market presence. According to Carbon Brief researches, France stands out as a leader in this shift; for the first time in 2022, heat pump sales surpassed those of gas and oil boilers, marking a significant milestone. This upward trajectory continued into 2023, with heat pumps capturing 61% of the heating market, even as fossil fuel boiler sales plummeted by 23%.
Germany has also experienced a steady rise in heat pump market share, growing from around 10% in 2014 to 33% in 2023. Despite a thriving fossil fuel heating sector, the sales of heat pumps have remained strong enough to sustain this growth.
In Poland, the market share of heat pumps plateaued in 2023 but has still risen significantly to 40%, up from just 10% in 2018. The Netherlands has seen an impressive increase as well, with heat pumps reaching an 18% market share in 2023, compared to a mere 1% in 2014.
Italy’s heat pump market share, while more stable, contracted in 2023 following two years of growth. In the UK, heat pumps have tripled their market share over the past five years, albeit starting from a low base. Excluding air-to-air systems, around 60,000 units were sold in 2023, giving the UK a current market share of about 3%.
Overall, when examining these six key markets, which predominantly rely on gas boilers, the market share of heat pumps has tripled from around 8% in 2013 to 24% in 2023. This indicates a promising shift towards more sustainable heating solutions, despite the challenges faced.
Effective Communication Protocols for Heat Pump Integration
-
Modbus-RTU, Modbus-TCP: These widely used industrial protocols enable communication between heat pumps and HEMS. Modbus-RTU is typically used for serial connections, while Modbus-TCP allows for communication over IP networks, ensuring flexibility and reliability in data exchange.
-
SG Ready: This protocol supports grid interaction, enabling heat pumps to adapt their operation based on grid signals, such as demand response events. It helps optimize energy use and costs by aligning heat pump activity with grid needs.
-
EEBUS: EEBUS provides a framework for smart energy devices to communicate, allowing heat pumps to share data about energy consumption and operational status. This facilitates coordination with other smart home devices for enhanced energy management.
-
Open Automated Demand Response (OpenADR): OpenADR standardizes the communication of demand response signals, allowing heat pumps to automatically adjust their operation in response to utility requests. This integration aids in grid stability and enhances energy savings.
-
KNX: KNX is a standard for building automation. It enables seamless integration into smart home environments, allowing for coordinated control of energy systems.
Efficient communication protocols are crucial for integrating heat pumps into HEMS, ensuring interoperability, optimizing energy use, and enhancing grid stability.
Benefits of Integrating Heat Pumps with Home Energy Management Systems (HEMS)
Integrating heat pumps with Home Energy Management Systems (HEMS) offers numerous advantages that enhance both energy efficiency and overall comfort in residential settings. Here are some key benefits:
-
Enhanced Energy Efficiency: HEMS optimizes the operation of heat pumps by adjusting their performance based on real-time energy demand and availability. This ensures that the heat pump operates at peak efficiency, reducing overall energy consumption and lowering utility bills.
-
Intelligent Scheduling: HEMS enables automated scheduling of heat pump operations based on time-of-use tariffs, allowing the system to prioritize heating or cooling during times when energy prices are most favorable. This scheduling capability ensures optimal comfort while minimizing costs, as it can arrange heat pump operation during periods of lower electricity rates.
-
Maximizing Battery Storage: When integrated with battery storage systems, HEMS can store excess energy generated from renewable sources, such as solar panels, for later use. This ensures that homeowners can utilize renewable energy for heating and cooling, reducing reliance on grid electricity and lowering energy costs.
-
Dynamic Tariff Optimization: HEMS takes advantage of dynamic tariffs by adjusting heat pump operations according to real-time energy prices. This strategic approach allows homeowners to maximize savings by using energy during low-cost periods while reducing usage during peak pricing times.
-
Demand Response Participation: An integrated HEMS allows homeowners to participate in demand response programs, where the heat pump can be adjusted based on signals from the grid. This not only helps stabilize the grid but also rewards homeowners for reducing their energy consumption during peak demand times.
-
Comprehensive Energy Monitoring: HEMS provides real-time monitoring of energy usage across various devices, including heat pumps. Homeowners gain valuable insights into their energy consumption patterns, enabling them to make informed decisions about energy use and further optimize their systems.
-
Improved Indoor Comfort: The electricity generated by your solar panels can extract heat from the outside air and transfer it indoors.By intelligently managing the heating and cooling processes, HEMS, in conjunction with heat pumps with smart heating function, maintains consistent indoor temperatures that harmonize comfort with the best dynamic tariffs. This synergy not only enhances comfort but also reduces energy waste, fostering a more sustainable household.
The future of heat pumps and its integration
The integration of heat pumps is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increased adoption of renewable energy sources. Many homeowners are now combining heat pumps with solar photovoltaic systems, which not only enhances energy efficiency but also contributes to a substantial reduction in carbon footprints. This synergy allows households to maximize the use of renewable energy for heating and cooling, aligning with broader sustainability goals.
Smart home technologies are also playing a pivotal role in the trend towards heat pump integration. As more consumers embrace smart devices, the incorporation of heat pumps within Home Energy Management Systems (HEMS) has become increasingly common. This integration enables users to have better control over their heating and cooling systems, optimizing energy use based on real-time data and preferences.
Advanced control systems, powered by innovations in artificial intelligence and machine learning, are transforming how heat pumps operate. These sophisticated systems analyze real-time data to optimize heat pump performance, ensuring efficient operation even in fluctuating environmental conditions.
As sustainability becomes a key focus for organizations and individuals alike, heat pump integration aligns perfectly with these objectives by providing efficient and environmentally friendly heating and cooling solutions. The global market for heat pumps is witnessing remarkable growth, driven by the rising demand for energy-efficient solutions that address the challenges posed by climate change.
Discover the power of heat pumps with our app! Our AI-driven features help you make the most of your heating and cooling, reducing your energy bills and enhancing your home comfort. Start saving today and gain insight into your energy usage with our innovative heat pump technology!
📱App Store: https://apps.apple.com/us/app/enjoyelec/id6467418530
📱Google Play:https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.enjoyelec.hems
Connect with us at http://www.linkedin.com/company/enjoyelec for the latest updates, insights, and news. We look forward to engaging with you and sharing our journey towards a smarter energy future.🎉🎊
