Understanding Time-of-Use Tariffs: Optimizing Savings and Energy Efficiency
What are Time of Use tariffs?
Time of Use (TOU) tariffs are a type of pricing plan where the cost of electricity varies based on the time of day. This means that the price you pay for electricity can be different at different times. For example, electricity might be cheaper during off-peak hours, such as late at night or early in the morning, and more expensive during peak hours, like in the afternoon when everyone is using power.
The idea behind TOU tariffs is to encourage people to shift their energy use to times when demand is lower. This can help reduce the strain on the power grid and lower overall energy costs. By understanding when electricity is cheaper, you can plan your energy use, such as running appliances or charging electric vehicles, during these cheaper times, potentially saving money on your electricity bill.
The Evolution of Time-of-Use Tariffs
Time-of-Use (TOU) tariffs have a long history, dating back to the energy crises of the 1970s when countries like the UK faced severe energy shortages. During this period, it became clear that energy consumption needed to be better managed to balance periods of high and low demand.
Initially, the challenge was addressing the uneven distribution of energy supply. For example, nuclear power plants would produce electricity around the clock, but demand would drop significantly at night when most people were asleep. To tackle this, early TOU tariffs like Economy 7 were introduced. This tariff offered two distinct rates: a higher daytime rate and a lower nighttime rate, encouraging consumers to shift their energy use to cheaper, off-peak hours.
While TOU tariffs saw limited changes for many years, recent advancements in technology have revived and transformed them. The advent of smart meters has revolutionized how energy usage is tracked and managed. These devices provide detailed data, enabling more sophisticated TOU tariffs that offer flexible pricing options and significant savings for consumers. As a result, modern TOU tariffs are now more dynamic and tailored to meet today’s energy challenges.
Pros and Cons of Time of Use tariffs
Pros of Time of Use tariffs
-
Cost Savings: One of the main benefits of TOU tariffs is the opportunity to save money by using electricity during off-peak hours when rates are lower. Households can plan their energy use around cheaper times, such as running appliances or charging electric vehicles at night, leading to reduced energy bills.
-
Better Energy Management: TOU tariffs encourage smarter energy use by helping consumers understand how their consumption patterns impact costs. By shifting energy usage away from peak times, households can optimize their consumption and reduce their carbon footprint.
-
Eases Grid Demand: By spreading energy usage more evenly throughout the day, TOU tariffs help reduce the strain on the electricity grid during peak hours. This can lead to a more stable grid, fewer blackouts, and better use of renewable energy sources.
Cons of Time of Use tariffs
-
Limited Flexibility: Not all energy use can be shifted to off-peak times. Essential activities like cooking, heating, or cooling may need to occur during peak hours, leading to higher costs that may be unavoidable for some users.
-
Complexity: TOU tariffs can be more complicated to understand compared to standard flat rates. Consumers need to track time-based pricing, which might require extra attention and effort to make sure they are using energy during cheaper periods.
-
Potential for Higher Bills: If consumers are unable to shift their energy use to off-peak times, they might end up paying more with TOU rates compared to standard rates. For households that rely heavily on electricity during peak hours, TOU pricing could lead to unexpectedly higher bills.
What are different types of the ToU tariff?
As shown on the pictures, there are three main types: Time-of-Use (ToU) Tariffs, Static ToU tariff, and Dynamic ToU tariffs.
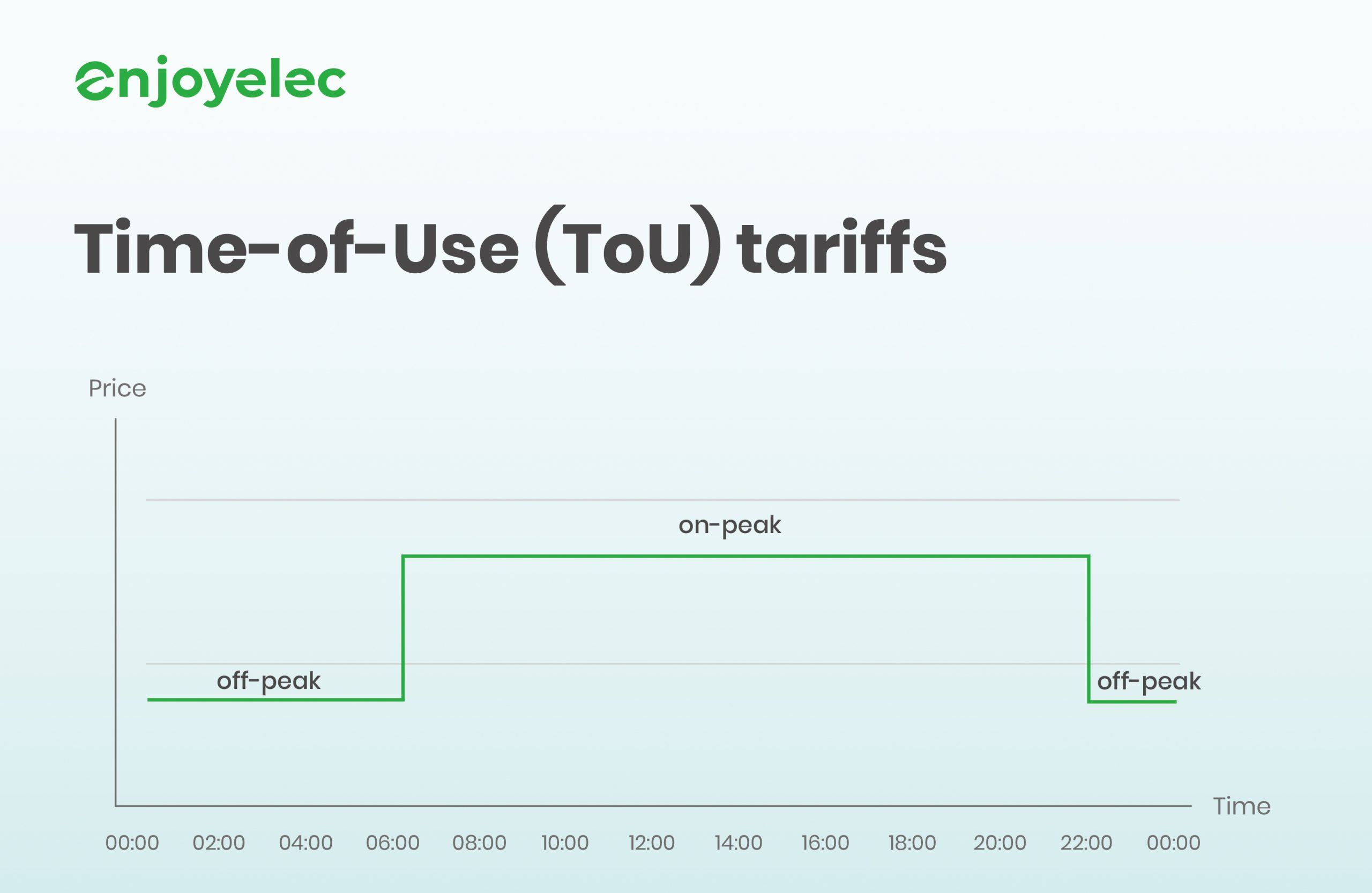
Time-of-Use pricing sets different rates for electricity based on fixed periods throughout the day. These rates are stable over longer durations and can be implemented without a smart meter, exemplified by day and night charges.
Static ToU tariff divides the day into fixed price periods. These periods, set inadvance and unlikely to change, are designed to mirror general trends in wholesale energy prices.
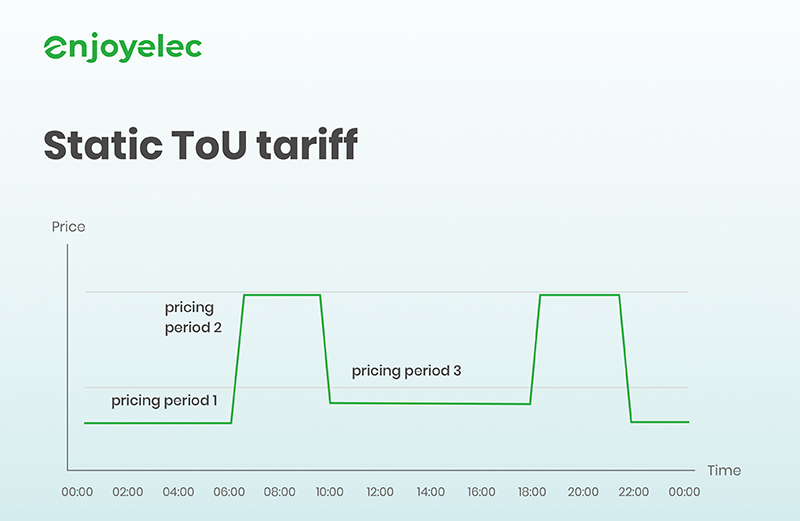
Dynamic ToU tariffs reflects wholesale market prices and updates daily, charging users based on actual consumption. lt requires smart metersand is preferred by EU regulators.
Time of Use Pricing VS Standard Rates
Time of Use (TOU) pricing varies the cost of electricity based on the time of day. Prices are generally lower during off-peak hours, such as late at night, and higher during peak times, like the late afternoon when electricity demand is high. For example, if you run your dishwasher at 10 PM, you might benefit from lower rates compared to running it at 6 PM.
In contrast, standard rates charge a consistent price per unit of electricity regardless of the time of day. This means you pay the same amount whether you use electricity at 2 PM or 2 AM. There is no variation in cost based on when you consume energy.
The main advantage of TOU pricing is the potential for cost savings by shifting your energy use to times when electricity is cheaper. Standard rates do not offer this flexibility, so you pay the same rate all the time without the opportunity to adjust your consumption for financial benefits.
ToU and HEMS
As households continue to adopt more heavy electrical load appliances, such as electric vehicles (EVs) and heat pumps, energy bills are expected to rise significantly. With these appliances consuming large amounts of electricity, managing energy consumption becomes more challenging and costly for homeowners. However, this also creates a significant opportunity to optimize energy use. By shifting the operation of flexible high-load devices, like EVs and home batteries, to times when electricity rates are lower, households can mitigate the impact of increased consumption without sacrificing convenience.
For instance, while it may be less flexible to shift the use of everyday household items like dishwashers or dryers, EV charging and battery storage present a different potential. These assets can be scheduled to charge during off-peak hours when energy is cheaper, allowing homeowners to significantly cut their electricity costs. This approach ensures that homes can continue to run essential appliances without dramatically increasing their energy expenses, while intelligently using higher-load assets when rates are more favorable.
DERs enable additional profits on ToU tariffs
Distributed Energy Resources (DERs) have revolutionized the way energy is consumed and managed, particularly in markets with ToU tariffs. These innovative systems, which encompass solar panels, battery storage, and smart appliances, empower consumers to harness the full potential of energy pricing dynamics, ultimately leading to additional profits.
ToU tariffs incentivize energy users to adjust their consumption patterns based on the varying costs of electricity throughout the day. DERs allow consumers to capitalize on this pricing structure by optimizing their energy usage and storage. By generating and storing electricity during off-peak hours when rates are low, DER owners can utilize this stored energy during peak hours, reducing their reliance on grid electricity at the highest cost. This not only cuts down on energy bills but also opens up avenues for arbitrage, where the difference in energy prices between off-peak and peak hours can be leveraged for profit.
Moreover, DERs enable seamless participation in demand response programs, where utilities reward customers for reducing their energy usage during peak hours. With automated control systems, DER owners can easily comply with these programs, earning monetary incentives and further boosting their profitability.
Beyond cost savings and incentives, DERs also enhance energy security and resilience. By reducing reliance on the grid during peak hours or in times of emergency, consumers can ensure a continuous supply of electricity, minimizing disruptions and associated costs.
In addition, DER owners can join Virtual Power Plants (VPPs), where their resources are aggregated to provide grid services and participate in wholesale electricity markets. This collaboration creates new revenue streams and contributes to a more stable and flexible grid, further solidifying the profitability of DER investments.
Navigating Negative Prices with ToU Tariffs
The rise of negative energy prices signals a transformative shift in our energy landscape, driven by an increased need for flexibility in balancing supply and demand. This phenomenon highlights the importance of adapting our energy consumption patterns to maintain grid stability and optimize costs.
Time-of-Use (ToU) tariffs present a strategic solution to this challenge. By incentivizing consumers to shift their energy use to periods of excess supply, ToU tariffs help mitigate the impacts of negative pricing and support grid stability. These tariffs encourage energy consumption during times when there is an abundance of power, thus reducing the frequency and severity of negative price scenarios.
Households equipped with smart energy management systems and energy storage solutions stand to benefit significantly from ToU tariffs. These technologies allow consumers to charge their batteries or use energy during low-cost, surplus periods. By doing so, they not only save on their electricity bills but also contribute to a more balanced and resilient grid.
In several European markets, the integration of ToU tariffs with automated systems has proven effective. Consumers can seamlessly take advantage of energy price fluctuations without major disruptions to their daily routines. This synergy between ToU tariffs and smart technology empowers households to navigate and benefit from the evolving energy landscape, ensuring both financial savings and support for grid stability.
Navigating Negative Prices with ToU Tariffs
The rise of negative energy prices signals a transformative shift in our energy landscape, driven by an increased need for flexibility in balancing supply and demand. This phenomenon highlights the importance of adapting our energy consumption patterns to maintain grid stability and optimize costs.
Time-of-Use (ToU) tariffs present a strategic solution to this challenge. By incentivizing consumers to shift their energy use to periods of excess supply, ToU tariffs help mitigate the impacts of negative pricing and support grid stability. These tariffs encourage energy consumption during times when there is an abundance of power, thus reducing the frequency and severity of negative price scenarios.
Households equipped with smart energy management systems and energy storage solutions stand to benefit significantly from ToU tariffs. These technologies allow consumers to charge their batteries or use energy during low-cost, surplus periods. By doing so, they not only save on their electricity bills but also contribute to a more balanced and resilient grid.
In several European markets, the integration of ToU tariffs with automated systems has proven effective. Consumers can seamlessly take advantage of energy price fluctuations without major disruptions to their daily routines. This synergy between ToU tariffs and smart technology empowers households to navigate and benefit from the evolving energy landscape, ensuring both financial savings and support for grid stability.
Different tariffs in different countries
Electricity pricing models vary significantly across Europe, driven by energy policies, market regulations, and smart meter adoption. According to the research from FlatPeak, let’s explore how different countries approach time-of-use (TOU) and dynamic tariffs.
United Kingdom
In the UK, TOU tariffs like Economy 7 and Economy 10 have become popular, particularly with the rollout of smart meters, which now cover 60% of households as of Q2 2024. Over half of UK consumers have adopted TOU tariffs, using lower off-peak rates, especially during nighttime, to reduce energy bills. The country’s strong emphasis on energy efficiency and grid stability has made TOU tariffs a core component of its energy strategy.
Germany
Germany’s focus on renewable energy through the Energiewende policy has sparked growing interest in dynamic pricing, though TOU tariffs are not as widespread as in the UK. Providers like Tibber are leading the charge with smart meters and dynamic tariffs that adapt to fluctuations in renewable energy production. While smart meter penetration is still low at around 3%, Germany has mandated that all energy suppliers offer at least one dynamic tariff, accelerating both smart meter adoption and grid balancing.
France
France’s long-standing Heures Creuses system offers reduced electricity rates during designated off-peak hours, with over two-thirds of residential customers benefiting from this model. Notably, the off-peak periods vary by region, allowing for localized pricing strategies to balance the grid more effectively.
Norway
Norway leads Europe—and likely the world—in dynamic tariff usage, with over 80% of consumers using day-ahead or intraday pricing models. Regional price variations are significant due to the country’s geography, with southern Norway often experiencing higher prices than the north. Norway also completed its smart meter rollout in 2023, achieving 99% coverage, making it a prime example of how dynamic tariffs can be integrated into national energy strategies.
Sweden
Sweden’s electricity market benefits from its reliance on hydroelectric and nuclear power, which keeps generation costs relatively low. While dynamic pricing only makes up about 40% of the overall electricity price, Sweden’s deregulated market fosters competition and efficiency. With smart meter coverage reaching 91% as early as 2010, the country continues to encourage dynamic and TOU tariffs to optimize energy use.
Italy
Italy’s electricity prices are higher than the European average due to its dependence on imported fossil fuels. Despite achieving 99% smart meter coverage by 2019, dynamic tariffs have been slower to take hold, as the rollout was initially focused on combating energy theft. However, Italy has required TOU tariffs for all residential customers since 2010, and recent market liberalization is starting to bring dynamic tariff options to the forefront.
Spain
Spain has made significant strides with smart meter deployment, reaching 99% coverage by 2018, and introduced mandatory two-tier TOU tariffs in 2021. Uniquely, Spain also penalizes peak consumption, encouraging households to shift energy use away from high-demand periods, adding an extra layer of incentive for efficient energy management.
Poland
Poland’s electricity prices remain among the lowest in Europe, largely due to its reliance on coal. However, to address EU pressure to reduce carbon emissions, Poland has adopted dynamic tariffs with 15-minute intervals, which is more granular than the typical hourly dynamic pricing seen in other European countries. Though smart meter rollout is still in progress, Poland’s dynamic pricing initiatives are a step toward a cleaner energy system.
ToU optimization in enjoyelec
In today’s energy landscape, Time-of-Use (ToU) optimization has become a key factor for both consumers and companies aiming to maximize energy efficiency and reduce costs. At enjoyelec, our Home Energy Management System (HEMS) and Controller leverage advanced technologies, including AI and direct device integration, to deliver precise and automated ToU optimization.
Our AI-powered HEMS takes a holistic approach to energy management, automatically optimizing home energy usage based on dynamic tariffs and price forecasts. For ToU optimization, our HEMS cloud layer makes forecast-based decisions by analyzing photovoltaic (PV) generation, consumption patterns, and price forecasts for the following day. These insights enable users to capitalize on lower electricity prices and avoid peak-rate periods. By automating energy management, HEMS reduces energy bills while ensuring comfort and convenience.
The enjoyelec HEMS Controller, serving as the core hub of our HEMS, seamlessly integrates with various energy devices, supporting multiple protocols like Zigbee, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, EEBUS, and OpenADR. Its AI cloud-edge synergy enables real-time energy management, ensuring that energy consumption aligns with ToU tariffs, even during brief internet outages. With offline functionality, our system continues to manage and optimize energy consumption based on pre-set ToU schedules.
For enhanced flexibility, users can set up to four distinct time periods (Off-Peak, Peak, Mid-Peak, and Super Off-Peak), each with unique pricing for weekdays and weekends. This allows households to take full advantage of ToU tariffs and minimize energy costs.
One of the key strengths of enjoyelec’s ToU optimization lies in direct integration with energy devices. We conduct rigorous testing and integration of each Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) and model. This direct connection ensures fast and reliable communication between the system and devices, providing immediate reaction to price fluctuations and consistent performance, even without internet access. Our Controller manages local control independently, ensuring that ToU costs are continuously optimized.
By using enjoyelec’s ToU optimization capabilities, households can automate their energy consumption, aligning it with the most cost-effective times of day. This not only drives substantial savings but also supports grid stability, helping users contribute to a more sustainable and efficient energy future.
Download the HEMS app now to learn more about how ToU tariffs help you save money:


Connect with us at http://www.linkedin.com/company/enjoyelec for the latest updates, insights, and news. We look forward to engaging with you and sharing our journey towards a smarter energy future.





