Unlock full potential of smart charging
Electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming more popular as new, affordable models are introduced, with major automakers investing heavily in their development. This growth presents opportunities and challenges, especially regarding grid strain from simultaneous charging. Smart charging systems help by optimizing energy use. This methodology tailors charging profiles, dynamically managing charging times and speeds while preventing grid congestion, ensuring adequate power supply, optimizing costs, and fostering renewable energy integration.
Different Layers of Smart Charging
-
Organizational layer
Who participates in EV Smart charging? Numerous stakeholders are integral to the development and functionality of smart electric charging systems. These key players include:
-
EV manufacturers
-
Utility Companies
-
Charge point operators
-
Energy Supplier
-
EV service Providers
-
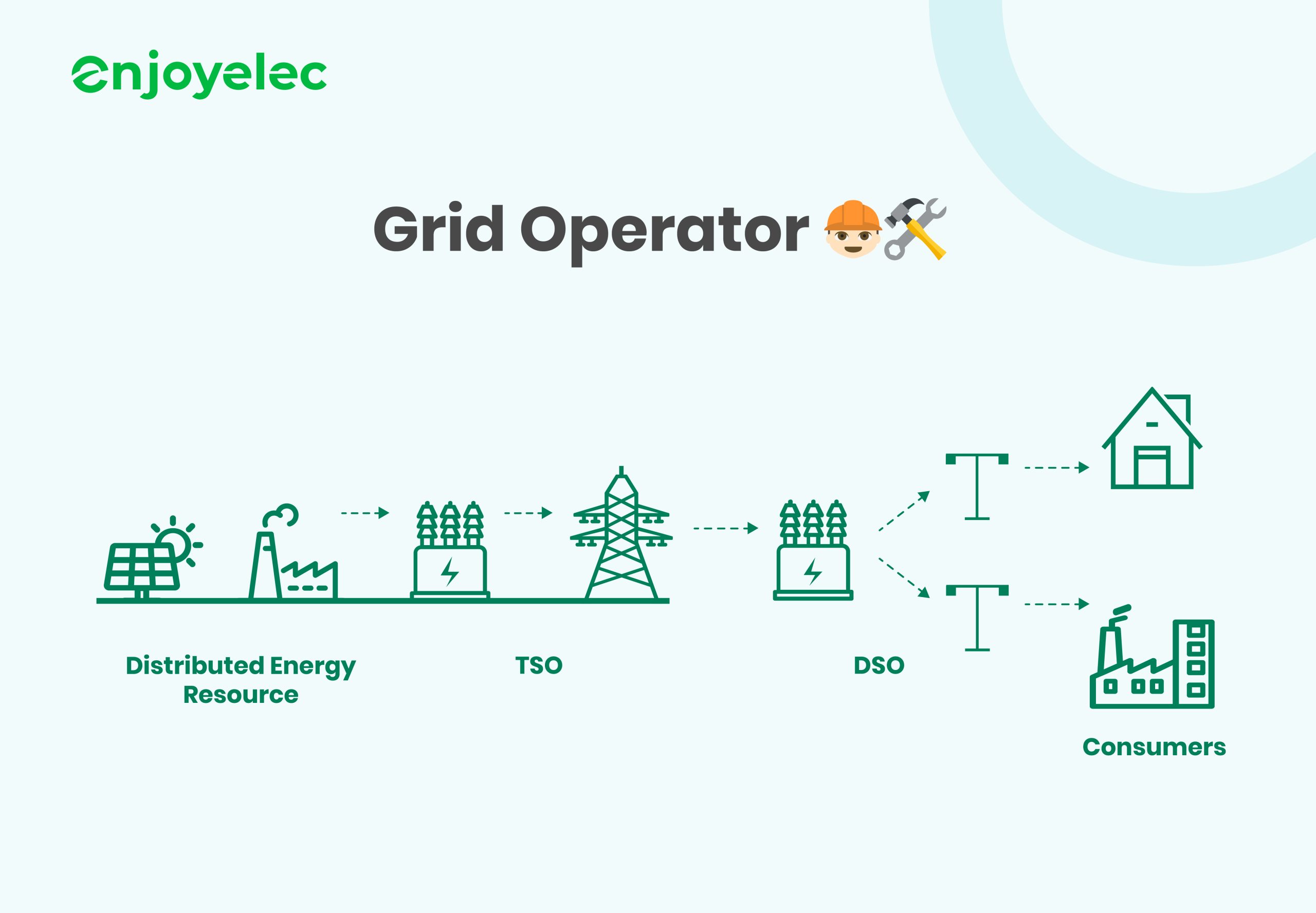
Grid Operators
-
Governments
-
EV drivers
Eeach of them have unique needs and interests when it comes to smart charging.
- Communication layer
Effective communication standards play a pivotal role in advancing smart charging solutions. These standards facilitate seamless data access, sharing, and collection across the EV ecosystem. The seamless integration of electric vehicles (EVs) into the charging ecosystem and the grid necessitates the employment of a diverse array of protocols, among which stand out OCPP, OpenADR, EEBUS, ISO 15118, IEC 61851, IEC 62196, IEC 62955and IEEE 2030.5,etc. These protocols and standards form the backbone of efficient smart charging systems, fostering seamless communication, universal compatibility, and the implementation of cutting-edge functionalities across disparate devices and platforms.
In the array of available protocols and standards, we support OCPP, EEBUS, IEC 62955 and IEC 61851. These protocols and standards are at the forefront of our commitment to delivering robust and efficient communication solutions within the smart charging ecosystem.
-
Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP) is a flexible communication standard that connects EV charging stations with backend systems. It ensures that both legacy and new charging stations can work together, supporting dynamic load management to alleviate stress on the power grid. This protocol plays a key role in transmitting control signals effectively, allowing for seamless communication between charging stations and management software, regardless of the manufacturer. By embracing open standards and fostering a collaborative, community-driven approach, enjoyelec ensures that its solutions remain at the cutting edge of technological advancements.
-
EEBUS is a standardized digital communication protocol. With EEBUS, our charger can be seamlessly integrated with other smart electric appliances in homes and buildings for more efficient energy usage. The seamless integration of EV charging solutions into the smart energy grid, championed by the EEBUS initiative, underscores enjoyelec’s dedication to embracing open standards and leveraging its expertise in innovative technologies.
-
IEC 61851 serves as a standardized framework for conductive charging systems utilized in electric vehicles. It encompasses the defining characteristics and operational parameters of EV supply equipment, outlines the specifications for the interconnection between this equipment and electric vehicles, and prescribes the mandatory electrical safety requirements that must be met by the EV supply equipment.
-
IEC 62955 applies to residual direct current detecting devices (RDC-DD) designed for permanently connected AC electric vehicle charging stations used in mode 3 charging (as per IEC 61851-1 and IEC 60364-7-722). These devices are referred to as Residual Direct Current Monitoring Devices (RDC-MD) or Residual Direct Current Protective Devices (RDC-PD).
-
Legal layer
The effective implementation of smart charging relies heavily on robust laws and regulations that define its scope and operation. Establishing a comprehensive legal framework is crucial for fostering cooperation among stakeholders.
An example of such regulations is the UK government introduced smart charging regulations effective from June 2022, mandating that every new private charge point sold in Great Britain, whether for domestic or workplace use, must integrate smart functionality. This requirement spans installations at residences, commercial establishments, and other private locations. Smart functionality empowers these charge points to communicate bidirectionally, react to signals to modify charging rates, and engage in demand-side response activities. This regulatory approach not only promotes efficient energy management but also supports grid stability and advances sustainable energy practices.
Smart Charging and Smart Power Grid
Smart Grid revolves around modernizing electricity networks to enhance efficiency, reliability, and sustainability. Unlike traditional grids, Smart Grids integrate advanced communication, monitoring, and control capabilities. These features enable real-time data exchange between electricity suppliers, consumers, and grid operators. Smart Grid technology empowers utilities to better manage electricity flow, respond to demand fluctuations, integrate renewable energy sources effectively, and optimize overall grid performance.
Smart Charging plays a pivotal role within the Smart Grid framework by optimizing the integration of electric vehicles (EVs) into the grid. As the adoption of EVs increases, so does the demand for electricity. Smart Charging solutions enable grid operators to manage this demand intelligently. By leveraging bi-directional communication between EVs, charging stations, and the grid, Smart Charging systems can adjust charging schedules based on grid conditions, electricity prices, and user preferences. This capability not only supports grid stability but also enhances efficiency and reduces operational costs.
To fully harness the potential of smart charging solutions and grid connectivity, collaboration among diverse stakeholders—governments, utility companies, technology developers, and consumers—is indispensable. This collective effort is essential for advancing the adoption of these technologies.
What benefits Smart charging delivers?
- Saving money
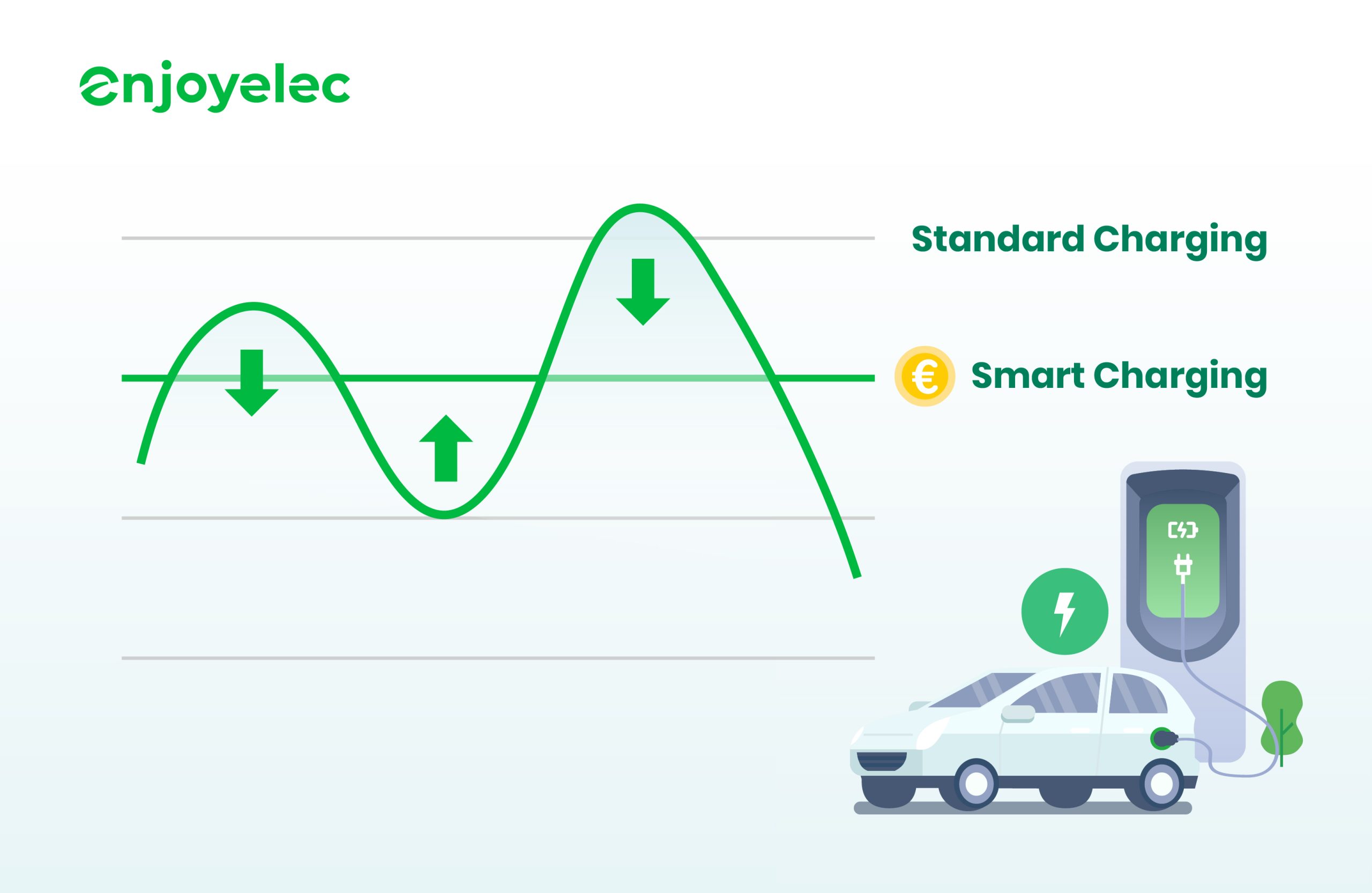
Drivers could schedule EV charging sessions during off-peak hours to save money on their electricity bill. Moreover, utility providers often incentivize off-peak EV charging with rebates or discounted rates, encouraging more economical and sustainable energy consumption practices. This approach not only benefits individual consumers by lowering their operational costs but also supports broader grid management strategies aimed at enhancing overall system efficiency.
- Enhancing Grid Stability
To mitigate grid stress, utilities strategically adjust charging rates across numerous chargers, effectively evening out peak demand periods. Furthermore, Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology enables EV batteries to feed power back into the grid, further bolstering stability.
- Boosting Grid Resilience
Integrating smart charging strategies transforms EVs into mobile energy assets, enhancing grid stability and reliability. This approach mitigates power disruptions by allowing EVs to store and supply electricity, ensuring a more resilient energy infrastructure.
-
Fostering Renewable Energy Integration
Smart charging optimizes EV charging times to coincide with peak renewable energy production, such as sunny or windy periods. This maximizes the use of clean energy, reduces reliance on fossil fuels, and lowers emissions. Additionally, smart charging can dynamically adjust to fluctuations in renewable supply, absorbing excess energy when available and reducing demand during shortages, thereby enhancing grid stability and efficiency.
How to get started with EV Smart Charging
Diving into Smart EV Charging might feel like an overwhelming task. However, it is much simpler than you think if you have the right strategy in place:
-
Step 1: Ensuring Seamless Smart Charging Setup
Firstly, it’s crucial to prepare thoroughly to ensure a smooth smart charging experience. Start by selecting an optimal location for your smart charge point, prioritizing easy accessibility for drivers, preferably with off-street parking availability. Moreover, ensure reliable connectivity is in place; smart chargers depend on stable Wi-Fi or mobile network connections to facilitate efficient data exchange. These steps lay a solid foundation for maximizing the effectiveness and convenience of your smart charging setup.
-
Step 2: Selecting the Right Charge Point
Now that you have the basics down, the next step is selecting the right charge point. Charge points offer two main options: tethered and untethered. Tethered models feature a permanently attached cable, while untethered ones require you to use your own. It’s essential to research different models thoroughly to find one that fits your particular needs. enjoyelec’s app is designed to accommodate various chargers, ensuring there’s an option suitable for different requirements and budgets.
-
Step 3: Optimize Smart Charging with the Right App
After installing your smart charge point, the next essential step is to download and install the enjoyelec app, which offers comprehensive charge point management functions. This app is free for home charging and empowers EV drivers with full control over their charging experience. Available on both the Google Play Store and the Apple App Store, enjoyelec enables you to effortlessly connect your charger to the internet with the full guide.
Once connected, you can intuitively configure it to suit your specific EV model and charging schedule, ensuring optimal performance and convenience.
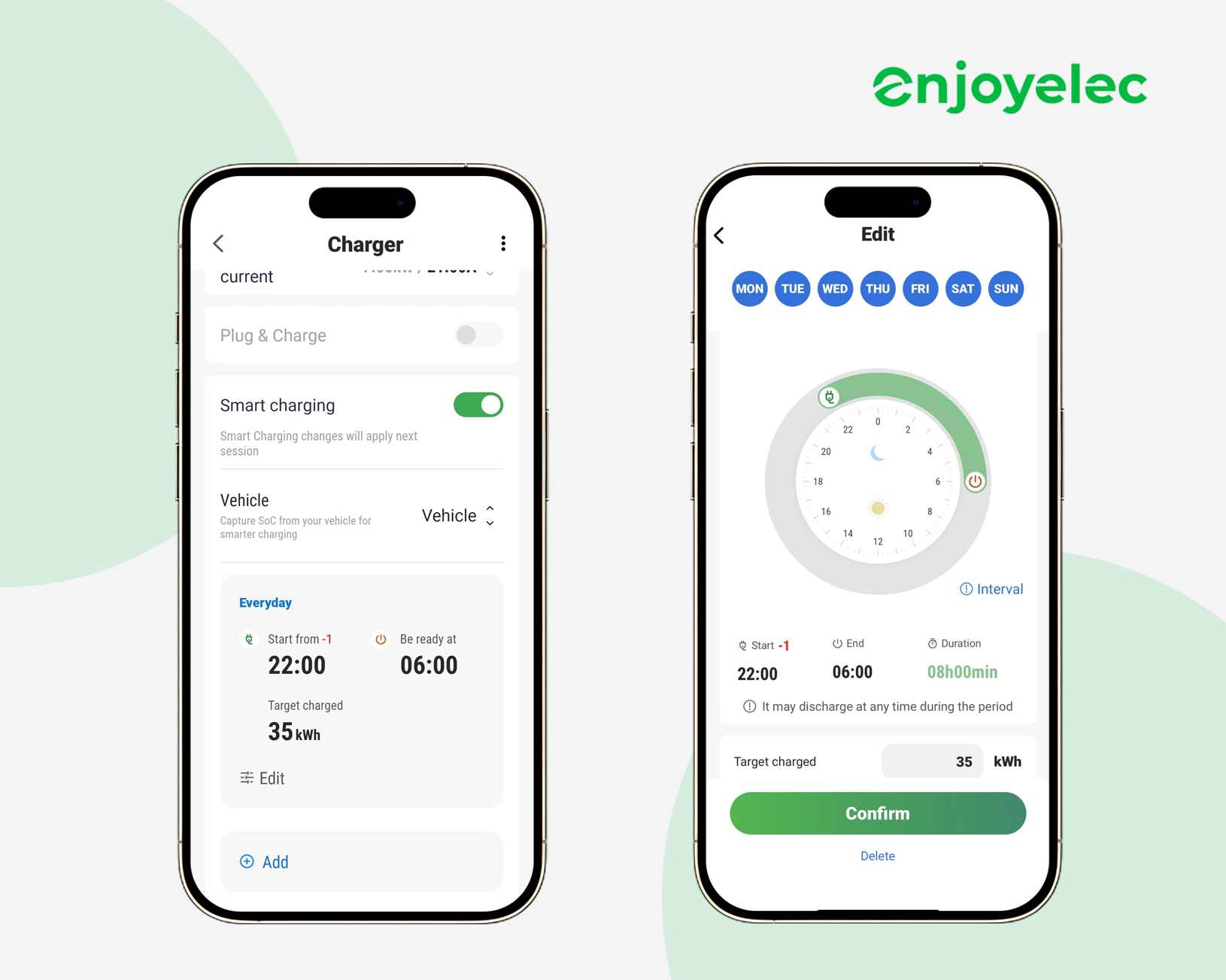
enjoyelec’s Features Connected to Smart Charging
-
Prioritize your charging needs: With enjoyelec App Smart Charging, you can set when your electric car should be fully charged and its target charge. Our system schedules charging to optimize renewable energy use, minimize costs, and ensure your vehicle is ready when you need it.
-
Charge your car at the lowest price: After connecting your vehicle to the enjoyelec app and setting your charging preferences, our algorithm schedules the charging process to optimize energy use for both green efficiency and cost-effectiveness during the entire charging period.
-
Free from overload: Optimizes charging by dynamically adjusting power levels according to your household’s energy usage, seamlessly transitioning between diverse modes to guarantee peace of mind and safeguard against any potential overloads.
-
Sell power to the grid: Users can participate in the electricity market’s ancillary services , selling surplus vehicle power back to the grid for profit. Ancillary services such as frequency regulation, voltage control, reserves, and black start capabilities ensure grid stability and integrate renewable energy effectively for a reliable electricity supply.
Future outlook of Smart Charging
The future of smart charging is closely tied to Virtual Power Plants (VPPs), which unify decentralized energy assets like EVs, solar panels, and batteries into a single, remotely controlled network. This integration allows VPPs to optimize energy use by charging EVs when renewable energy is abundant and discharging during peak demand, boosting grid stability and maximizing renewable energy utilization.
As VPPs become essential for energy resilience, they offer crucial grid services such as frequency regulation, vital for stabilizing grids increasingly reliant on renewables. Economically, smart charging reduces energy costs for consumers and eases the strain on utility infrastructure investments, paving the way for a resilient, cost-effective, and sustainable energy future.
While EVs may appear individually limited in flexibility, their collective integration into VPPs enhances their impact, providing essential demand response flexibility. The market potential for VPPs, especially those utilizing residential EVs, is vast but largely untapped, presenting significant opportunities for businesses to capitalize on this potential and create substantial value.
The next evolution in smart charging is bidirectional charging, known as V2G (Vehicle-to-Grid), V2H (Vehicle-to-Home), or V2X (Vehicle-to-Everything). This technology allows electric vehicles to serve as energy storage units. EVs can discharge stored power to homes or feed it back into the grid. They can support the grid during peak demand periods or store surplus renewable energy generated locally for later use.
While these technologies are currently in experimental stages, further development is essential to optimize their efficiency and ensure widespread adoption.
Connect with us at http://www.linkedin.com/company/enjoyelec for the latest updates, insights, and news. We look forward to engaging with you and sharing our journey towards a smarter energy future.🎉🎊